Block Types
Blocks are the building units of your simulation. Connect them to model data flow and calculations.
Variable
Example: FIRE Basic →An uncertain input sampled from a probability distribution. Each iteration draws a new value.
Properties
Example
Project duration with Triangular distribution: min=10, mode=15, max=25 days.
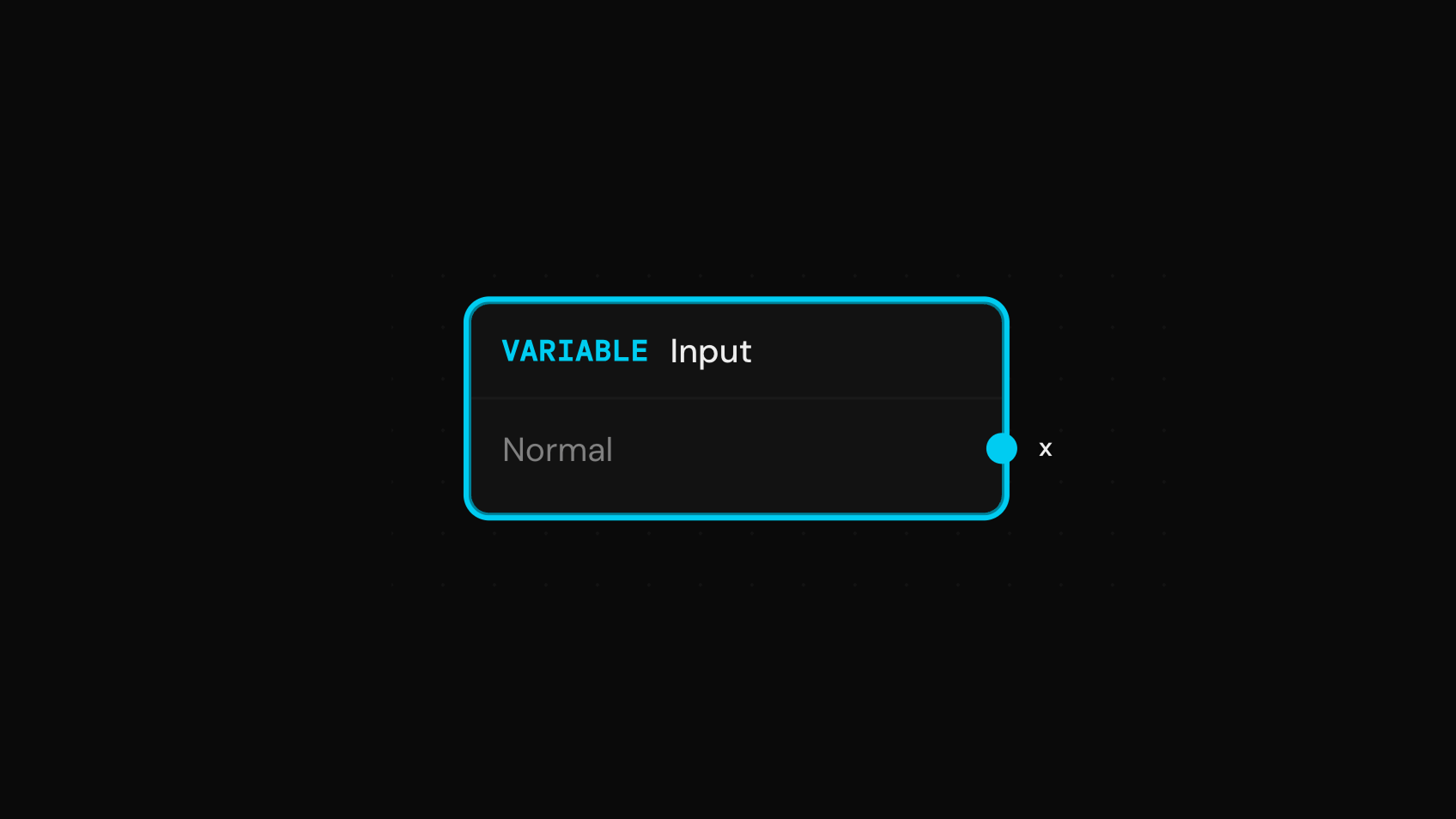
Constant
Example: Project Risk →A fixed value that remains the same across all iterations. Use for known parameters and assumptions.
Properties
Example
Tax rate set to 0.25 (25%).

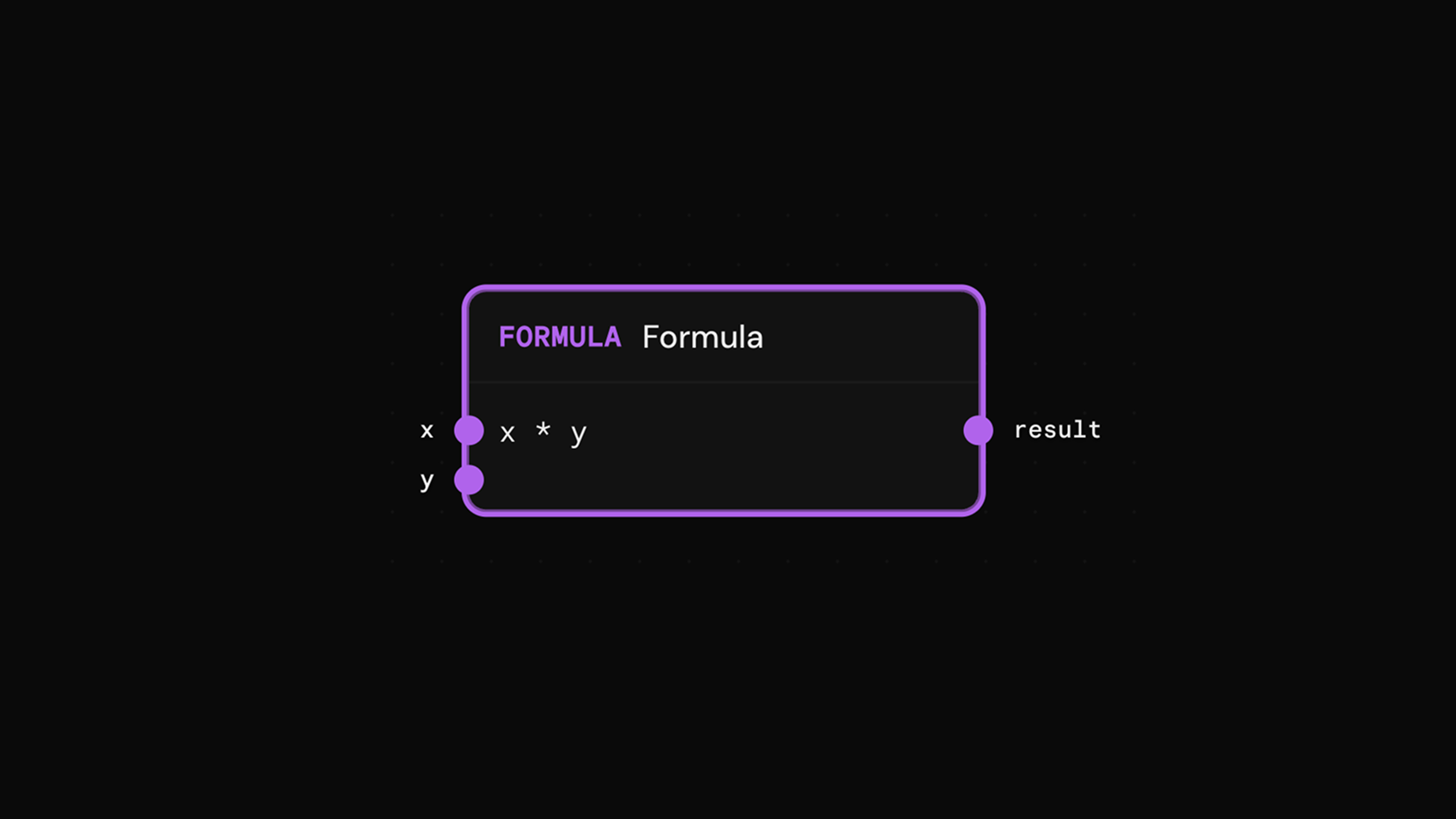
Formula
Example: FIRE Basic →Computes a value from connected inputs using mathematical expressions. Input ports are created automatically based on variables in the expression.
Properties
Example
Expression: revenue - cost - (revenue * tax_rate)
Output
Example: FIRE Basic →Marks a value for inclusion in results. Connect final calculations here to generate histograms and statistics.
Properties
Example
Connect Net Profit to see its distribution after simulation.
Decision
Compares two inputs and routes flow based on the result. Outputs different values for true and false conditions.
Properties
Example
If revenue > threshold, output revenue; otherwise output 0.

Aggregator
Combines multiple inputs using Sum, Average, Min, Max, or Product. Accepts any number of connections.
Properties
Example
Sum all department budgets into Total Budget.

Copula
Example: Weather Sales →Models statistical dependence between variables. Applies correlations while preserving each variable's marginal distribution.
Properties
Example
Two stocks with ρ=0.7: when one rises, the other tends to follow.

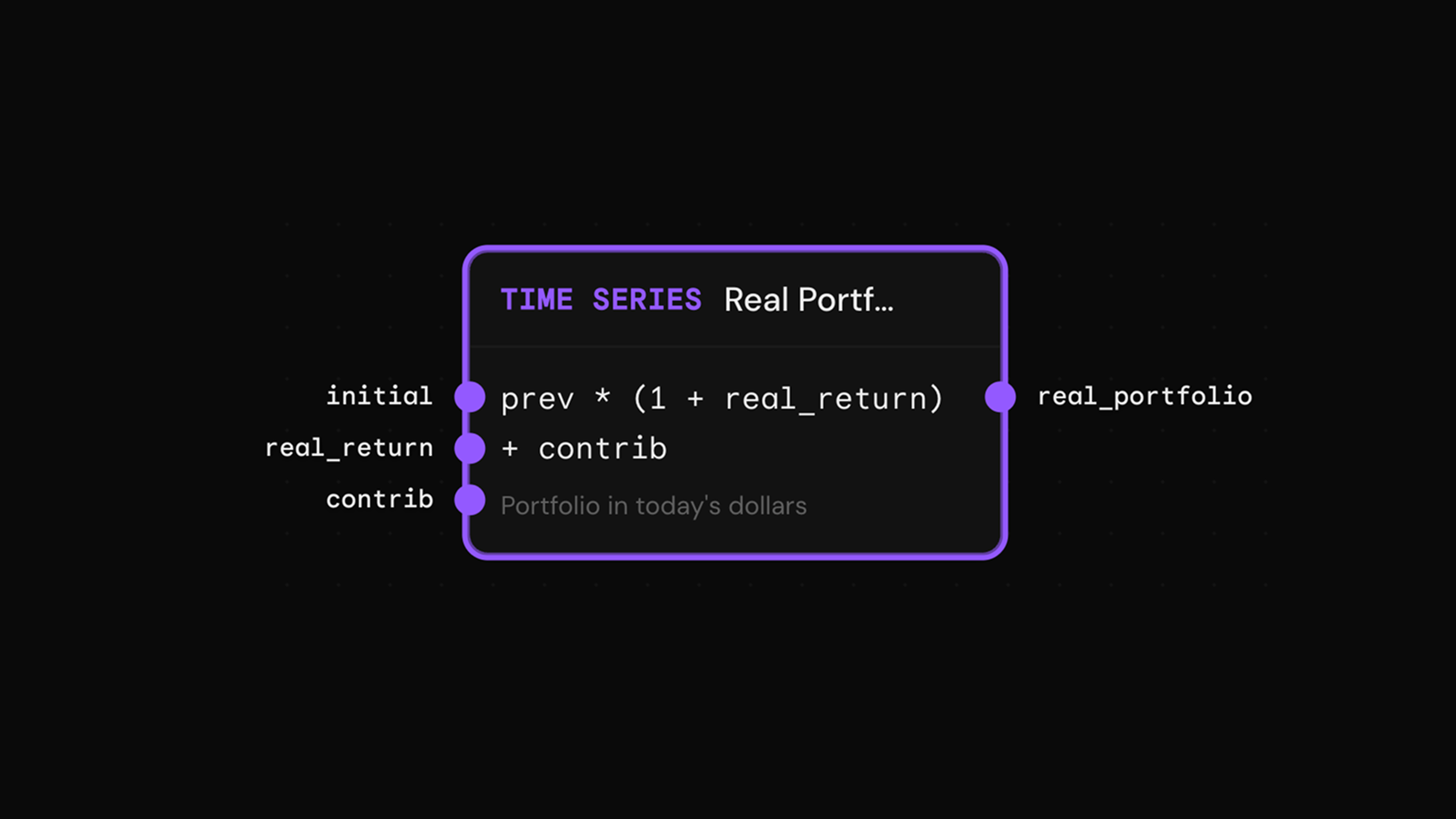
Time Series
Example: FIRE Advanced →Models values evolving over time. The expression can reference the previous value using 'prev' to create dynamic paths.
Properties
Example
Portfolio growth: prev * (1 + return) + contribution
Annotation
Example: FIRE Basic →A documentation note. Does not affect calculations or have ports.
Properties
Example
Document assumptions, data sources, or methodology.